Testicles are one of the most sensitive organs in male body, so it’s very important not to ignore even minor pain. The reasons of unpleasant sensations can be more serious than you think, starting from a cyst and finishing by varicose veins. Find out what the ten common causes of testicle pain are, and how to deal with them.

- Inguinal hernias are pretty widespread among men, but not all of them know what they are. In fact, hernias can occur in any body part, but usually tend to develop when a part of fatty tissue or intestine squeezes through (often, the abdominal wall).
If you have pain in testicles, it may be caused by inguinal hernia taking place in the seam between the thigh and the body. Painful sensation happens when hernia moves inside. It starts in the abdomen and finishes developing in the scrotum: this is the same way testicles travelled as they separated from the abdomen when you were a fetus. The location of discomfort and pain is where the hernia ends.
The only way to get rid of hernia is a surgery. Don’t postpone it, as hernias can grow and develop with the time being, and pain won’t go away with the time being.
- Testicular cancer. Luckily, testicular pain doesn’t necessarily mean you have cancer: only 1 man out of 10 experiences pain with cancer. However, you should become concerned about it, if you palpate a lump in testicles. Pain usually appears when the tumor has grown considerably, and can also be accompanied by the feeling of heaviness, swelling or visual enlargement of a testicle. Symptoms of testicular cancer can also include pain in abdomen or lower back, chest tenderness, and collection of fluid in the scrotum. If you notice any changes in testicles, visit a doctor. It is crucial to determine testicle cancer early.
- Testicular torsion. This is a case that requires immediate medical help, so if you have testicular torsion, call emergency right away. This condition takes place when the spermatic cord twists and closes blood flow to testicles. Wonder if you’ll notice it? In fact, the pain is so strong that you’re unlikely to ignore this agony even if you fall asleep. Leaving this condition untreated may leave you without a testicle, so you should contact emergency and go through a surgery immediately.
If it’s possible to save a testicle, surgeons will re-position it and stitch to the inside of the scrotum to prevent twisting down the road. The same will be done with the second testicle. Although it sounds awful, operation is the only way to prevent such a horrible pain.
- Hematocele. Every man gets kicked or bitten in testicles at least once, and knows what it’s like to feel this unbearable pain. As a rule pain sets in, and everything is okay, but sometimes there can be dangerous complications, and hematocele is one of them.
Testicles are located in a multi-layered sac, and its damage can cause blood collecting between the layers. A hematocele can be eased by just taking rest, but sometimes can require drainage and a minor surgery. Everything depends on how strong the discomfort is and the source of bleeding. If a hematocele hasn’t been caused by exterior damage, then the doctor will search for some other reason.
- Inflammation of the epididymis. This is a coiled tube located in the back part of each testicle. It is responsible for storage, maturity and delivery of sperm. It can get inflamed because of bacteria that usually get into urethra and back. Bacteria can get inside either because of STDs like gonorrhea or Chlamydia, or be coli form (bacteria living in the intestine). Less often, viral infections can cause infestation.
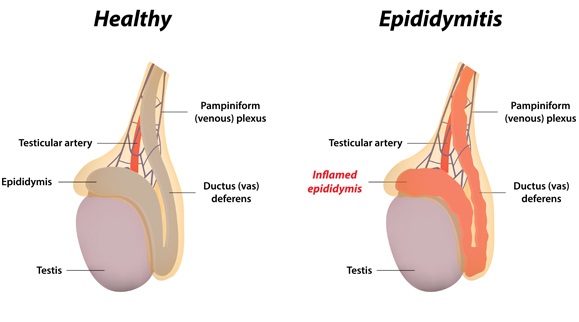 When the inflammation develops, testicles usually swell and turn red. Pain can be especially acute during ejaculation or bowel movements. Besides, a man can have blood in the urine and experience a frequent need to urinate. Chills also take place.
When the inflammation develops, testicles usually swell and turn red. Pain can be especially acute during ejaculation or bowel movements. Besides, a man can have blood in the urine and experience a frequent need to urinate. Chills also take place.
As a rule, this condition can be simply cured by antibiotics. More serious inflammations are treated with a surgery. Don’t postpone visit to doctor, if you have symptoms of epididymitis.
- Varicose veins in testicles – a common condition in men. If you feel a mass in your testicles that stops causing discomfort when you sit down, you should visit a doctor. Men having swollen or knotted veins in testicles describe this feeling like a bag of worms or spaghetti.
When valves of veins fail, blood collects inside and causes pain that can get worse from day to day. While the varicoceles grow it becomes more noticeable. For anatomical reasons, varicoceles tend to appear on the left testicle. A minor surgery (removal of obstructed veins) and anti-inflammatory drugs can cure the disease.
- The epididymis is not the only type of inflammation causing pain in testicles. A spermatocele (cyst) growing in the epididymis can also be the reason. This cyst can be benign, and it starts growing in the head of the epididymis. Most of time, they are small-sized and don’t cause any symptoms and pain, but as a spermatocele grows to several centimeters, it can lead to the feeling of heaviness and unpleasant sensations.
As a rule, a spermatocele doesn’t require medical treatment, especially if it’s not cancerous and doesn’t grow. When a man has pain and discomfort, he will be prescribed antibiotics. In fact, it is better to remove a spermatocele as it may lead to infertility.
- Orchitis is a serious swelling of the testicles that can be caused by epididymitis and different infections (mumps, STDs, or brucellosis). This disease causes serious side effects: blood in semen, increased pain during movement of testicles and penis. Swelling during orchitis can have different sources, and it’s important to cure it with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Orchitis conditioned by mumps may result into sterility, and it can also lead to shrinking of the testicles. During treatment, scrotum should be kept elevated.
- Kidney stones. This disease can also indirectly affect your testicles and lead to pain that projects downward. If these stones are not too big, a man will only need to take pain medications and drink a lot of water. There is nothing to be done with testicles.
- Testicular rupture happens when the protective membrane around testicles rips and blood gets into the scrotum. As a rule, membrane is damaged after sport injuries, traumas and car crashes. If you go through a surgery within 72 hours after the trauma, there’s a 80% chance that your testicle will be saved. Therefore, if you have pain after damage of testicle (even if it’s not visible), don’t hesitate to call a doctor.
In-time diagnosis is the key to your male health. Pain in testicles never appears out of nothing. If it bothers you, visiting a doctor is the smartest idea.







